H.264 Codec: Motion estimation settings
Motion Estimation (M.E.) is the process of estimating the motion of parts of an image between consecutive frames of a video. This helps reduce the amount of data by storing only the changes or movements between frames, rather than fully encoding each image.
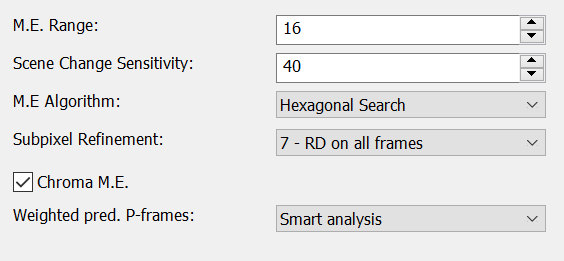
M.E. Range (Motion estimation Range)
The M.E. range determines how large the search area for motion estimation can be. This means that the codec looks for movements within a specified frame around a reference pixel. A larger M.E. range increases the accuracy of motion estimation, but can also affect computing power and compression efficiency.
The typical value range is from 16 to 64

Advertisement
Scene Change Sensitivity
<Scene changes occur when there is an abrupt change in the image content between two consecutive frames
The value affects how sensitive the codec is to scene changes. Typically this value is set from 0 to 100
Specifies how big the difference from one frame to the next frame must be for an I-frame to be inserted.
- Low value (e.g. 0): The codec is less sensitive to scene changes. It only inserts keyframes when the image content has changed significantly.
- High value (e.g. 100): The codec is very sensitive and recognizes even small changes in the image content as scene changes. This results in keyframes being generated more frequently, which can increase bitrate consumption but can also improve playback quality, especially in scenes with rapid changes.

M.E. Algorithm (Motion Estimation Search Algorithm)
The Motion Estimation Search Algorithms in the libx264 codec are crucial for the efficiency and quality of video compression. They determine how the motion between frames is estimated to generate P-frames. Different search methods such as Diamond Search, Hexagon Search and Full Search offer different trade-offs between accuracy and computational effort.
- Diamond ( fastest )
- Hexagon
- Multi hex
- Exhaustive ( slow )
- SATD Exhaustive ( very slow )

Advertisement
Subpixel Refinement
Subpixel refinement in the libx264 codec is a powerful tool for improving motion modeling in video compression. It increases the accuracy of motion estimation, providing better image quality and more efficient compression by capturing finer motion details between adjacent frames. This feature is particularly useful in scenes with subtle motion or fine textures, where traditional integer-pixel motion estimation may be inaccurate.
- 0 - Fullpel only
- 1 - QPel SAD
- 2 - QPen SATD
- 3 - HPel on MB then QPen
- 4 - Always QPen
- 5 - QPen & Bidir ME
- 6 - RD on I/P frames
- 7 - RD on all frames
- 8 - RD refinement on I/P frames
- 9 - RD refinement on all frames
- 10 - QP-RD
Chroma M.E. (Chroma Motion Estimation)
Chroma Motion Estimation (Chroma M.E.) is a technique used in video compression, particularly when encoding video with the libx264 codec. It refers to estimating the motion of color components (chroma) of an image, as opposed to the brightness component (luma), which is traditionally given more focus.
By taking color information into account when estimating motion, compression becomes more efficient, resulting in better use of available storage space.
If Chroma Motion Estimation is deactivated, only the brightness information is used to determine the direction of movement.
If Chroma Motion Estimation is activated, brightness and changing colors are used to determine the direction of movement.

Weighted prediction P-frames
The Weighted Prediction P-Frames feature in the libx264 codec is a method to improve video compression, especially in the prediction of P-frames (predicted frames).
- Disabled
- Blind offset
- Smart analysis