XMedia Recode: H.264 Encoder Settings | Tips and Techniques
The H.264 codec, also known as AVC (Advanced Video Coding), is a widely used video compression standard that was developed in 2003 by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and ISO/IEC as part of the MPEG-4 standard. It is used for the efficient encoding of video and provides a high compression rate while maintaining good video quality. H.264 is used in a variety of applications, including streaming services, video calls, Blu-ray discs, and many other media formats.
Advertisement
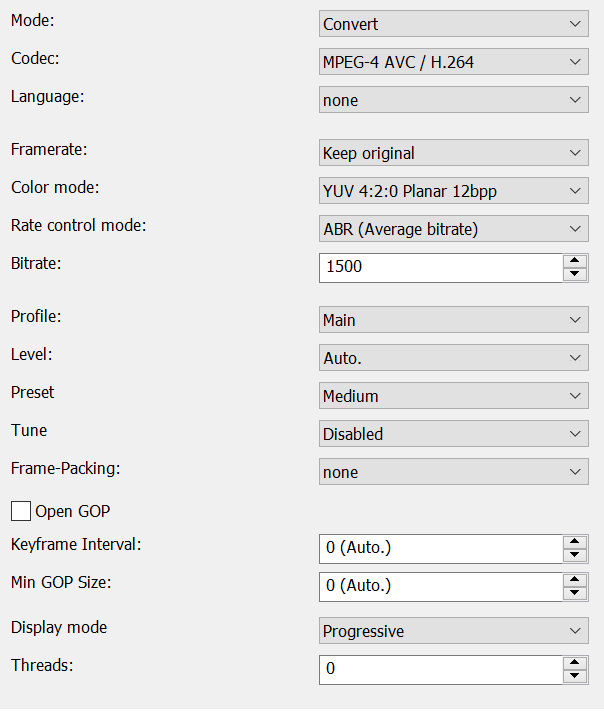
Mode
- Convert (convert video stream)
- Copy (copy video stream)
Codec
Determines which video codec to use for encoding.
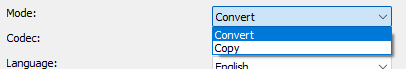
Language
Sets the language that displays when playing the player.
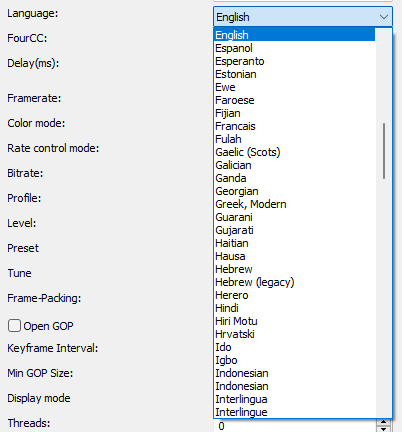
Delay(ms)
Sets the delay of the video stream.
Positive values start the stream later.
Negative values start the stream earlier.
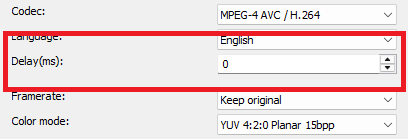
FourCC
Is a 4-byte identifier which specifies the format of a video stream.
Profile
The profile setting in the H.264 codec is crucial for finding the right balance between complexity, compatibility, and quality. Depending on the use case (e.g., streaming, professional video recording, or simple video conferencing), the appropriate profile is selected to ensure optimal performance and compression. A High Profile offers very high quality and is suited for more demanding applications, while the Baseline Profile is optimized for simple and resource-constrained devices.
- Baseline
- Main
- High
- High 4:2:2
- High 4:4:4
- High 10
- High 4:2:2 10
- High 4:4:4 10

Level
The level setting defines the limits for various parameters, such as the maximum resolution, maximum bitrate, and the number of reference frames that can be used in a given encoding.
Higher levels require more powerful hardware, both for encoding and decoding.
| Level | resolution/frame rate | maximum video bitrate Baseline Extended Main |
maximum video bitrate High |
maximum video bitrate High 10 |
maximum video bitrate High 4:2:2 High 4:4:4 |
| 1 | 128×96 / 30 | 64 kbit/s | 80 kbit/s | 192 kbit/s | 256 kbit/s |
| 1b | 176×144 / 15 | 128 kbit/s | 160 kbit/s | 384 kbit/s | 512 kbit/s |
| 1.1 | 176×144 / 30 320×240 / 10 352×288 / 7.5 |
192 kbit/s | 240 kbit/s | 576 kbit/s | 768 kbit/s |
| 1.2 | 176×144 / 60 320×240 / 20 352×288 / 15 |
384 kbit/s | 480 kbit/s | 1152 kbit/s | 1536 kbit/s |
| 1.3 | 320×240 / 40 352×288 / 30 |
768 kbit/s | 960 kbit/s | 2304 kbit/s | 3072 kbit/s |
| 2 | 320×240 / 40 352×288 / 30 |
2 Mbit/s | 2,5 Mbit/s | 6 Mbit/s | 8 Mbit/s |
| 2.1 | 352×288 / 50 352×576 / 25 |
4 Mbit/s | 5 Mbit/s | 12 Mbit/s | 16 Mbit/s |
| 2.2 | 352×288 / 50 720×480 / 15 |
4 Mbit/s | 5 Mbit/s | 12 Mbit/s | 16 Mbit/s |
| 3 | 720×480 / 30 720×576 / 25 |
10 Mbit/s | 12,5 Mbit/s | 30 Mbit/s | 40 Mbit/s |
| 3.1 | 720×576 / 60 1280×720 / 30 |
14 Mbit/s | 17,5 Mbit/s | 42 Mbit/s | 56 Mbit/s |
| 3.2 | 1280×720 / 60 1280×1024 / 42,2 |
20 Mbit/s | 25 Mbit/s | 60 Mbit/s | 80 Mbit/s |
| 4 | 1280×720 / 68,3 1280×1024 / 48 1920×1080 / 30 |
20 Mbit/s | 25 Mbit/s | 60 Mbit/s | 80 Mbit/s |
| 4.1 | 1280×720 / 68,3 1280×1024 / 48 1920×1080 / 30 |
50 Mbit/s | 62,5 Mbit/s | 150 Mbit/s | 200 Mbit/s |
| 4.2 | 1280×720 / 145 1920×1080 / 64 2048×1080 / 60 |
50 Mbit/s | 62,5 Mbit/s | 150 Mbit/s | 200 Mbit/s |
| 5 | 1920×1080 / 72,3 2048×1080 / 67,8 3672×1536 / 26,7 |
135 Mbit/s | 168,75 Mbit/s | 405 Mbit/s | 540 Mbit/s |
| 5.1 | 2048×1080 / 112,9 3840×2160 / 31,7 4096×2160 / 28,5 |
240 Mbit/s | 300 Mbit/s | 720 Mbit/s | 960 Mbit/s |
| 5.2 | 2048×1080 / 172 3840×2160 / 66,8 4096×2160 / 60 |
240 Mbit/s | 300 Mbit/s | 720 Mbit/s | 960 Mbit/s |
Advertisement
Preset
Sets parameters to balance compression efficiency with encoding speed
- ultrafast
- veryfast
- faster
- fast
- Medium
- slow
- slower
- veryslow
Tune
The tune function in H.264 (libx264) is an option that allows the user to optimize the encoding for specific scenarios or requirements.
- Disabled
- Film (Optimized for movies or other videos with high image quality and low motion content)
- Animation (Optimized for animated content)
- Grain (Used when the video contains graininess or noise.)
- Stillimage (Optimized for still images, slideshows or other static content)
- Psnr (Optimized for accurate PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio) measurement)
- Ssim (Optimized for measuring SSIM (Structural Similarity Index))
- Fastdecode (Optimized for fast video decoding)
- Zerolatency (Used to achieve extremely low latency, which may be required for real-time transmissions such as video calls or live streaming)
- Touhou
Frame - Packing
Set frame packing mode for Stereoscopic content.
- none
- checkerboard = pixels are alternatively from L and R
- column alternation = L and R are interlaced by column
- row alternation = L and R are interlaced by row
- side by side = L is on the left, R on the right
- top bottom = L is on top, R on bottom
- frame alternation = one view per frame

Framerate
Specifies the output video rate.
Open GOP
Open GOP (Open Group of Pictures) is a technique in video compression where the frames in a Group of Pictures (GOP) can access frames from the next GOP. This means that the last frame of a GOP can rely on reference data from the GOP that follows it, allowing for more efficient compression.
Vorteile
- Better compression:
By referencing adjacent GOPs, the file size can be reduced and compression efficiency improved.
- Better image quality:
Open GOP can often lead to higher image quality because it provides more image data for compression.
Advertisement
Min GOP (Group Of Pictures) length
Minimum GOP length, the minimum distance between I-frames.
Keyframe Interval
This determines the maximum distance between I-frames
Very high GOP lengths will result in slightly more efficient compression, but will make seeking in the video somewhat more difficult
Display mode
- Progressiv
- Interlaced TFF (Top field first)
- Interlaced BFF (Bottom field first)
Color mode
Specify output colorspace format.
Threads
Enables parallel encoding by using more than 1 thread to increase speed on multi-core systems
