AOM AV1-Codec settings in XMedia Recode: Tips and Techniques
The AV1 (AOMedia Video 1) codec is a modern, royalty-free video compression standard specifically designed for efficient video transmission and storage. It was developed by the Alliance for Open Media (AOM), an international consortium group that includes companies such as Google, Mozilla, Amazon, Netflix, Microsoft and many others.
Advertisement
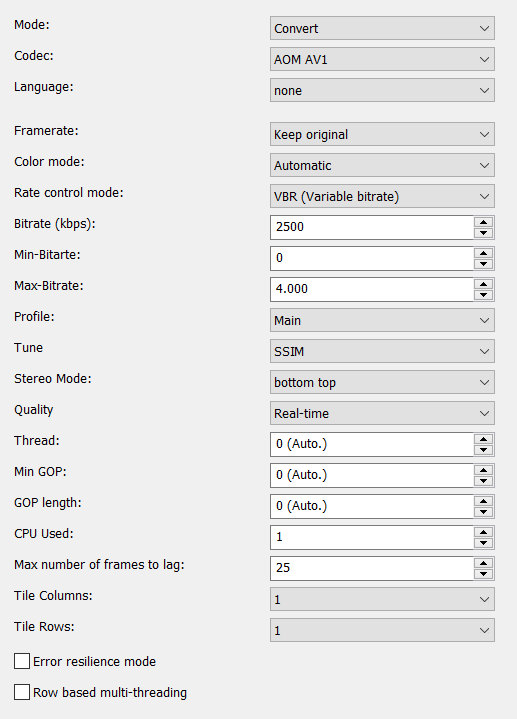
Mode
- Convert (convert video stream)
- Copy (copy video stream)
Codec
Determines which video codec to use for encoding.
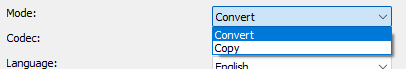
Language
Sets the language that displays when playing the player.
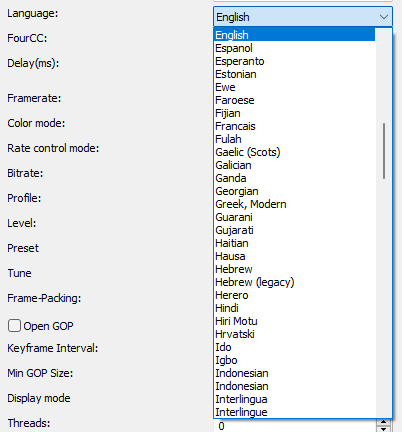
Framerate
Specifies the output video rate.
Level
The Level setting sets the limit for various parameters such as the maximum resolution, the maximum bitrate and the max tiles that can be used in an encode.
Higher levels require more powerful hardware, both for encoding and decoding.
| Level | Resolution/Frame Rate | maximum video bitrate Main |
maximum video bitrate High |
Max Tiles | Max Tile Cols |
| 2.0 | 426×240 / 30fps | 1.5 Mbit/s | - | 8 | 4 |
| 2.1 | 640×360 / 30fps | 3.0 Mbit/s | - | 8 | 4 |
| 3.0 | 854×480 / 30fps | 6.0 Mbit/s | - | 16 | 6 |
| 3.1 | 1280×720 / 30fps | 10.0 Mbit/s | - | 16 | 6 |
| 4.0 | 1920×1080 / 30fps | 12.0 Mbit/s | 30.0 Mbit/s | 32 | 8 |
| 4.1 | 1920×1080 / 60fps | 20.0 Mbit/s | 50.0 Mbit/s | 32 | 8 |
| 5.0 | 3840×2160 / 30fps | 30.0 Mbit/s | 100 Mbit/s | 64 | 8 |
| 5.1 | 3840×2160 / 60fps | 40 Mbit/s | 160 Mbit/s | 64 | 8 |
| 5.2 | 3840×2160 / 120fps | 60 Mbit/s | 240 Mbit/s | 64 | 8 |
| 5.3 | 3840×2160 / 120fps | 60 Mbit/s | 240 Mbit/s | 64 | 8 |
| 6.0 | 7680×4320 / 30fps | 60 Mbit/s | 240 Mbit/s | 128 | 16 |
| 6.1 | 7680×4320 / 60fps | 100.0 Mbit/s | 480 Mbit/s | 128 | 16 |
| 6.2 | 7680×4320 / 120fps | 160.0 Mbit/s | 800.0 Mbit/s | 128 | 16 |
| 6.3 | 7680×4320 / 120fps | 160.0 Mbit/s | 800.0 Mbit/s | 128 | 16 |
Profile
Limit the profile of the output stream.
- Main
- Professional
- High
Tune
The tune function in the AOM AV1 codec optimizes the encoding for certain quality metrics
- PSNR: This setting aims to maximize the PSNR
- SSIM: This setting aims to maximize the SSIM
- IQ (image quality): This setting takes into account the overall visual image quality and not just mathematical metrics such as PSNR or SSIM
Stereo Mode
Stereo Mode allows the AV1 codec to encode stereoscopic content (that which contains two separate images for the left and right eye) more efficiently. It processes the visual content so that both perspectives (right and left) are compressed in a way that maintains visual quality while reducing file size.
- none
- mono
- left right
- bottom top
- top bottom
- right left
Quality
With the AOM AV1 codec, the Quality function determines whether speed or quality is the priority
- Real-time (Fast processing and low resource consumption, with slightly poorer quality)
- Good (Better quality than real-time with a moderate compromise in speed)
Min GOP (Group Of Pictures) length
Minimum GOP length, the minimum distance between I-frames.
Keyframe Interval
This determines the maximum distance between I-frames
Very high GOP lengths will result in slightly more efficient compression, but will make seeking in the video somewhat more difficult
CPU Used
This setting allows you to determine how intensively the CPU is used for video encoding.
0: This is the lowest value and means that the encoding is performed with the highest possible quality and the lowest possible resource consumption. The algorithm uses very little parallelization and does not intensively use all CPU cores. The encoding is slower, but the result is of the highest quality.
7 and 8: These values represent the highest optimization for speed and maximize the use of CPU resources. At these settings, encoding will be significantly faster, but quality may be noticeably compromised. These values are mainly suitable for scenarios where speed is more important than quality, such as real-time streaming or fast video processing tasks.

Max Number of Frames to Lag
This setting affects how many frames the encoder can consider in its look-ahead buffering to make predictions and find the optimal encoding for the compressed frames.
In video coding, it is common for a frame to be encoded not only based on the information from the previous frame (for I-frames) or the neighboring frames (for P-frames and B-frames). The encoder can "look" at multiple frames to find the best encoding strategy for future frames.
The encoder can work more efficiently by including more future frames, resulting in a higher compression rate without compromising visual quality.
Color mode
Specify output colorspace format.
Threads
Enables parallel encoding by using more than 1 thread to increase speed on multi-core systems
Tile Columns
Tiling splits the video into rectangular regions, which allows multi-threading for encoding and decoding.
The number of tiles is always a power of two. 0=1 tile, 1=2, 2=4, 3=8, 4=16, 5=32.
Advertisement
Tile Rows
The Tile Rows setting determines the number of vertical "tile" rows into which the image is divided.
The number of tiles is always a power of two: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32.
The more tile rows you choose, the more parallel processing units can be used, which generally improves encoding performance, especially on multi-core processors.
Error Resilience Mode
In real-time video applications or streaming protocols like WebRTC or DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP), enabling the Error Resilience Mode ensures that the video can continue to play even with occasional packet loss or network jitter, making it more reliable in less-than-ideal network conditions.
Row-Based Multi-Threading
Row-Based Multi-Threading in the AV1 codec is a parallel processing technique for video frames that aims to increase the efficiency and speed of video decoding by having multiple threads work simultaneously on different parts of a frame.

Enable Frame Parallel Encode
The "Enable Frame Parallel Encode" feature in the AV1 codec allows multiple frames of a video to be encoded in parallel, resulting in faster processing. This technique efficiently uses multi-core processors, shortens encoding time, and improves scalability, especially when processing large or high-resolution video data.

