Opus - Codec settings
The Opus codec is a sophisticated, lossy audio compression algorithm specifically designed for real-time communications, streaming, and other variable-bit-rate applications. Opus combines the best features of two other well-known codecs, SILK (for voice transmission) and CELT (for music and wide-spectrum audio), to provide high flexibility and exceptional quality. It was developed by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) and is available under the open source BSD license.
Opus is characterized by its ability to deliver excellent audio quality across a wide range of bit rates, from 6 kbps to 510 kbps, while dynamically adapting to network conditions and the type of audio source. This makes it particularly suitable for applications such as VoIP (Voice over IP), video conferencing, online gaming, music streaming, and podcasting.
A standout feature of the Opus codec is its low latency, which is crucial for real-time applications such as video and voice communications. It also offers high robustness against network loss, making it ideal for unreliable networks such as cellular networks and Wi-Fi. Opus also supports a wide range of audio channels, from mono to multi-channel surround sound (5.1 or 7.1).
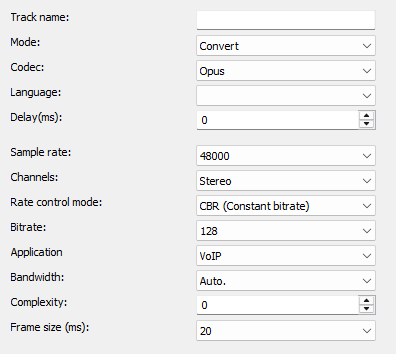
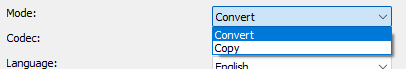
Mode
Specifies whether the audio track is converted or copied.
Advertisement
Codec
Specifies which audio codec is used for encoding.
Language
Sets the language that the player displays when playing.
Delay(ms)
Sets the delay of the audio stream.
Positive values start the stream later.
Negative values start the stream earlier.
Sample rate
Specifies the sample rate.
The higher the sample rate, the richer the sound. The values are between 8000 and 48000 Hz.
Advertisement
Bitrate
Sets the bitrate. A higher bit rate improves the sound quality but also increases the size of the file. Values are between 32 and 1152 kbps.
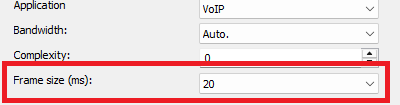
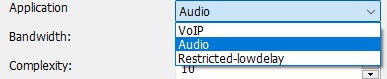
Application
-
VoIP:
Gives best quality at a given bitrate for voice signals. It enhances the input signal by high-pass filtering and emphasizing formants and harmonics. Optionally it includes in-band forward error correction to protect against packet loss. Audio:
Gives best quality at a given bitrate for most non-voice signals like music. Use this mode for music and mixed (music/voice) content, broadcast, and applications requiring less than 15 ms of coding delay.- Restricted-lowdelay
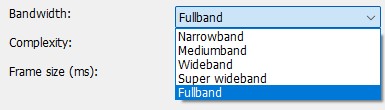
Bandwidth
Sets the maximum bandpass. But still gives the encoder the freedom to reduce the bandpass if the bitrate gets too low to achieve better overall quality.
- Narrowband (8 kHz)
- Mediumband (12 kHz)
- Wideband (16 kHz)
- Super wideband (24 kHz)
- Fullband (48 kHz)
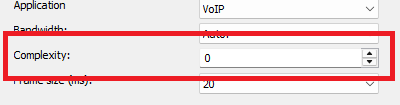
Complexity
Sets the computational effort from 0 to 10,
- 0 = fast (lower quality)
- 10 = slow (highest quality)
Channels
- Mono
- Stereo
- 5.0
- 5.1
Frame size (ms)
Specifies how many milliseconds of audio are processed per frame.
Smaller values = lower latency, larger values = better compression efficiency.
Here: 20 ms, a good default value for streaming and recording (low latency with stable quality).