FDK AAC - Codec settings: Tips and Techniques
The FDK AAC (Fraunhofer FDK AAC) codec is a highly advanced audio codec that is primarily used for the efficient compression of audio data in the AAC (Advanced Audio Codec) format. It was developed by Fraunhofer IIS (Institute for Integrated Circuits), a leading institute in the field of audio technology.
The codec supports a wide range of audio formats, including various AAC profiles such as LC-AAC (Low Complexity), HE-AAC (High Efficiency AAC) and AAC-LD (Low Delay).
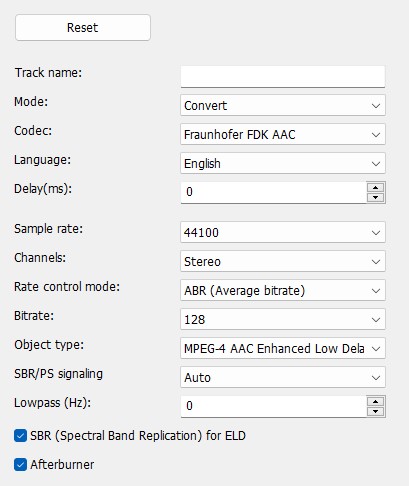
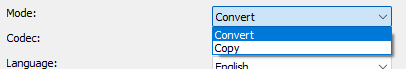
Mode
Specifies whether the audio track is converted or copied.
Advertisement
Codec
Specifies which audio codec is used for encoding.
Language
Sets the language that the player displays when playing.
Delay(ms)
Sets the delay of the audio stream.
Positive values start the stream later.
Negative values start the stream earlier.
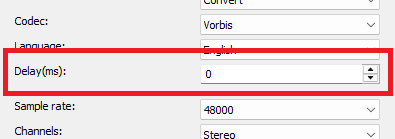
Sample rate
Specifies the sample rate.
The higher the sample rate, the richer the sound. The values are between 8000 and 96000 Hz.
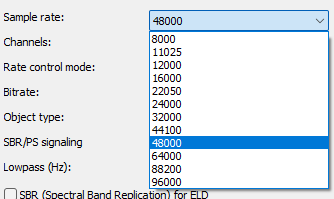
Channels
- Mono
- Stereo
- 3.0
- 4.0
- 5.0
- 5.1
- 6.1
- 7.1
Rate control mode
- ABR
- Qualität ( 1 bis 5)
Bitrate
Sets the bitrate. A higher bit rate improves the sound quality but also increases the size of the file. Values are between 32 and 1152 kbps.
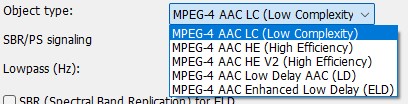
Objekt-Type
- MPEG-4 AAC LC (Low Complexity)
- MPEG-4 AAC HE (High Efficiency)
- MPEG-4 AAC HE V2 (High Efficiency)
- MPEG-4 AAC Low Delay (LD)
- MPEG-4 AAC Enhanced Low-Delay
SBR/PS signaling
The SBR/PS setting in the FDK AAC codec helps the codec to efficiently compress audio content without significantly compromising the perception of audio quality at low bit rates.
- Implicit backwards compatible signaling
- Explicit SBR, implicit PS signaling
- Explicit hierarchical signaling
Implicit Backwards Compatible Signaling
The bitstream contains a mix of classic AAC information and enhanced SBR/PS data. A decoder that does not have the capabilities to decode SBR/PS (i.e. an older AAC decoder) will treat the bitstream data as if it were a normal AAC stream. A modern decoder (such as the FDK AAC Decoder with support for HE-AAC) will recognize and use the SBR/PS data for enhanced playback.
This method is backwards compatible because older decoders will not cause an error and will still be able to decode the bitstream, but without the benefits of SBR/PS.
Explicit SBR, Implicit PS Signaling
The bitstream contains explicit indications of the use of SBR (e.g. additional bandwidth information for the upper frequency range) and simultaneously carries the PS data without explicit marking. Modern decoders that support both SBR and PS can extract and use this data to improve the audio quality, while older decoders can make do with the standard AAC data rate.
This method offers some flexibility as it is suitable for decoders that support SBR as well as those that only support basic AAC.
Explicit Hierarchical Signaling
The bitstream is structured hierarchically, with the basic AAC data transmitted first, followed by the SBR data, and then the PS data. A decoder that supports both SBR and PS can decode this data in the correct order and hierarchy to produce higher quality audio. A decoder that does not support any of the advanced features will only process the basic data and be limited to traditional AAC playback.
This method offers the highest flexibility and control over signal processing because both techniques (SBR and PS) are transmitted explicitly and in a structured manner, maximizing compression while improving decoder efficiency.
Lowpass
Sets the low pass filter with the specified cutoff frequency in Hertz.
If "0" is entered, a low-pass filter is automatically set.
Advertisement
Afterburner
The Afterburner feature in the FDK AAC codec is a performance-optimized technology that increases compression efficiency and improves audio quality at low bit rates.
It is recommended to always enable this if additional memory usage and processing power consumption are not a problem.

SBR (Spectral band replication) for ELB
SBR for ELD is a technique that allows the codec to efficiently reconstruct the high frequencies of an audio signal to improve the perceived audio quality while keeping the bitrate low. It involves dividing the audio stream into two regions: a low-frequency (lower) region that is directly encoded and a high-frequency (upper) region that is reconstructed by SBR.
This technology is particularly suitable for applications such as VoIP or conferences where high voice quality with low delays is required.